Best Defensive Investment Strategy (Defensive Investment Strategies)
Forget gold and options: This Factor-Based Strategy Is the Ultimate Crisis-Proof Investment (plus trend/following).
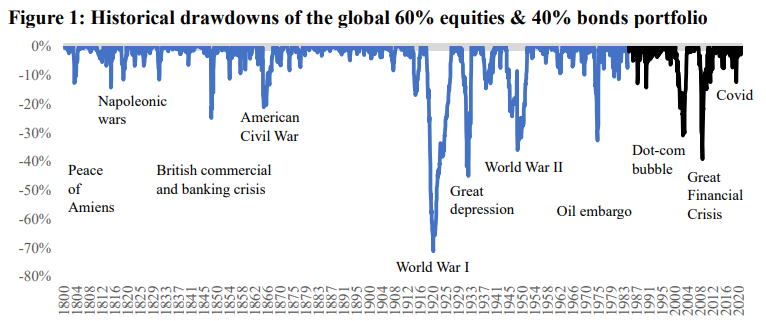
A common investment strategy involves balancing risk and return with a traditional portfolio split: 60% stocks (equities) and 40% bonds (the 60/40 portfolio). While this portfolio has delivered strong returns over the long haul (about 7.0% per year over 222 years), it is severely vulnerable to market crashes, just like stocks. Bonds can fall hard when the interest rates go op, and sometimes it happens in a bear market for stocks.
Historically, these “drawdowns” (peak-to-trough losses) can be massive; the global 60/40 portfolio once lost 71.2% between 1800 and 2021. When you lose 50%, you must gain 100% just to break even, illustrating the destructive power of volatility drag. As recently as 2022, the 60/40 portfolio suffered a nasty drawdown.
Related reading: –The best defensive asset class
A new paper, “The best defensive strategies: two centuries of evidence,” authored by Guido Baltussen, Martin Martens, and Lodewijk van der Linden, tackled this challenge head-on. By analyzing over 220 years of global financial data, the researchers determined the most effective, stress-tested strategies for protecting an investment portfolio during downturns.
The core finding? Multi-asset defensive strategies offer the most robust downside protection.
The Two Champions of Downside Protection
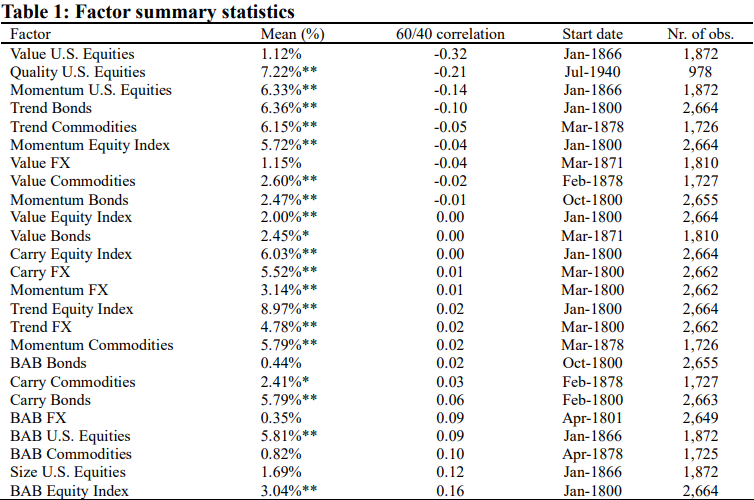
The research found that two advanced strategies, one based on behavioral “factors” and the other based on price trends, are highly successful at protecting investors from catastrophic losses, even across wildly different economic periods (including wars, gold standards, and high-inflation eras).
The paper looked at several investment portfolios:
1. Defensive Absolute Return
This strategy is an enhanced version of the Defensive Absolute Return (DAR) portfolio.
How it Works: The initial concept of DAR was to identify various financial “factors” (such as value, carry, or momentum) based on their correlation (or relationship) with the 60/40 portfolio. The strategy then aims to hedge the 60/40 portfolio by taking a long position in factors with the most negative correlation and a short position in those with the most positive correlation. This construction results in a portfolio that maintains a strong negative correlation (beta) to the traditional 60/40 portfolio.
The Improvement: Because the original design aimed for zero long-run return (which could lead to drawdowns during prolonged bull markets), the authors refined it into the DAR strategy. This enhanced approach goes long 40% of the best defensive factors and short 20% of the worst factors.
- This slight shift successfully preserves the strong defensive properties.
- It also adds a positive long-run return component (2.3% per annum for 5% volatility over the full sample).
- DAR4020 provided the best average protection in the worst 10% of 60/40 months (returning 1.0% per month).
2. Trend-Following Strategies
Trend-following involves systems that generally buy assets whose prices are moving up and sell assets whose prices are moving down across diverse markets, including equities, bonds, currencies, and commodities.
- Trend-following strategies performed very well during recessions and crisis periods since 1880.
- It provided the highest long-run positive return among the defensive strategies analyzed (4.8% per annum for 5% volatility).
Why Combining Them Is the Ultimate Defense
While both strategies are effective individually, they are complementary, meaning they perform well during different phases of a market decline, making their combination superior.
| Defensive Property | DAR | Trend-Following |
| Response Time | Immediate protection (Runs at a negative structural beta). | Slower response (Needs time for a declining trend to establish). |
| Bull Market Returns | Tends to have small losses. | Tends to have higher returns. |
| Short, Sharp Crises | Highly effective. During the quick COVID drawdown (Feb-Mar 2020), DAR4020 gained +5.0%. | Less effective initially. During the same COVID period, trend-following returned -1.1%. |
When combined in a 50/50 portfolio, the mix of DAR and trend-following significantly improved defensive characteristics compared to using either strategy alone.
For investors using the traditional 60/40 portfolio, adding the 50/50 combination as a hedge dramatically improved performance metrics: average losses during drawdowns exceeding 20% were reduced from 37.6% (60/40 standalone) to 15.1%.
What About Traditional Hedges?
The study also evaluated other popular defensive tools using the deep 222-year historical sample:
- Gold is Unreliable: Gold proved to be less effective than the factor strategies or trend-following, delivering negative average excess returns in the worst 60/40 months. It showed poor defensive properties even during the Classical Gold Standard era (1870–1914).
- Put Options are Too Costly: Buying put options (insurance against steep market drops) is effective during immediate, sharp downturns but comes with the heavy cost of negative long-run performance (“negative carry”), making them prohibitively expensive over the long term.
- Treasuries are Historically Inconsistent: Holding safe-haven government bonds was found to be historically unreliable over the two-century period, often failing to hedge equity losses. For the full 1800–2021 sample, Treasuries showed negative average performance during the largest equity drawdowns.
- Traditional Equity Factors (Low-Risk, Quality, Value): These factors consistently provided meaningful downside protection, with Low-Risk and Quality stocks performing especially well when the broader equity market was falling. However, DAR4020 generally proved superior across all defensive metrics when competing against them.
In conclusion, the research confirms that defensive investing principles are robust across radically different historical regimes. The most effective path to protecting a portfolio against severe downside risk involves leveraging the power of multi-asset factor strategies, specifically the enhanced DAR strategy, ideally combined with complementary trend-following.